


By increasing the precision dynamic electric flow balance adjustment, the medium-temperature water no longer requires the use of plate heat exchangers, reducing heat exchange losses. This leads to a decrease in the overall energy consumption of the chiller, saving approximately 20.2 million kWh of electricity annually.


The workshop's heat recovery system extracts high-temperature air, which was previously cooled directly to approximately 15°C using chilled water—resulting in excessive chilled water consumption. To improve efficiency, a pre-cooling air handling unit (AHU) was installed, utilizing a circulating tap water system for preliminary cooling. This reduces the load on the chiller and decreases electricity consumption, saving approximately 6.4 million kWh of electricity annually.


The large amount of concentrated alkali waste liquid from intermediate product cleaning is recovered and used for acid gas removal in the tail gas tower. This not only saves on tail gas treatment chemicals but also reduces wastewater treatment costs.

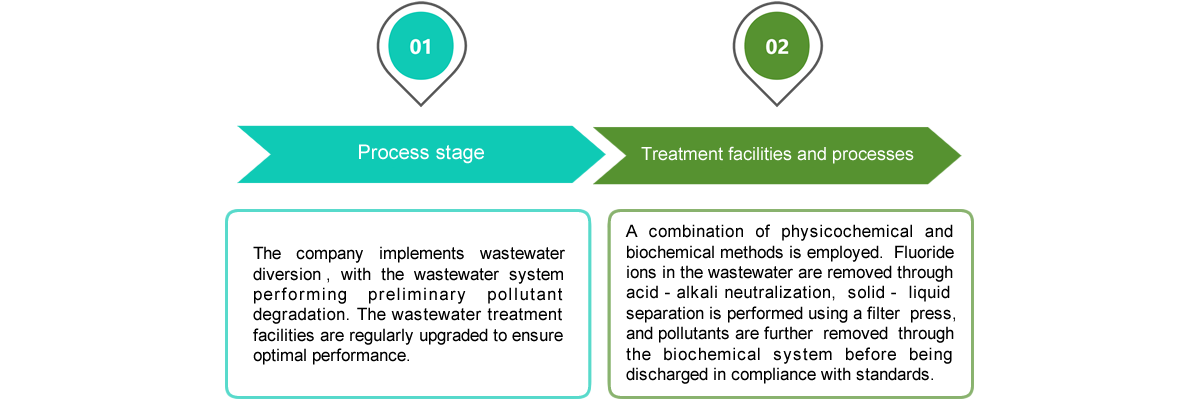
The original process involved discharging high-ammonia nitrogen wastewater to the wastewater station for biochemical treatment. This process, due to the needs of microbial growth and metabolism, consumes a large amount of carbon source and liquid alkali to treat the wastewater to meet discharge standards. To reduce operational chemical costs and increase the revenue from by-products, the MVR project has been initiated.


Strictly implement the company's solid waste management system, strengthen employee training, and enhance environmental awareness and standardized operational capabilities.


Strictly enforce the classification and separate storage of hazardous waste and general solid waste, eliminate mixed storage, and reduce the generation of hazardous waste.

The company entrusts qualified organizations to regenerate and reuse hazardous waste activated carbon. General solid waste is recycled and utilized by qualified third-party organizations.